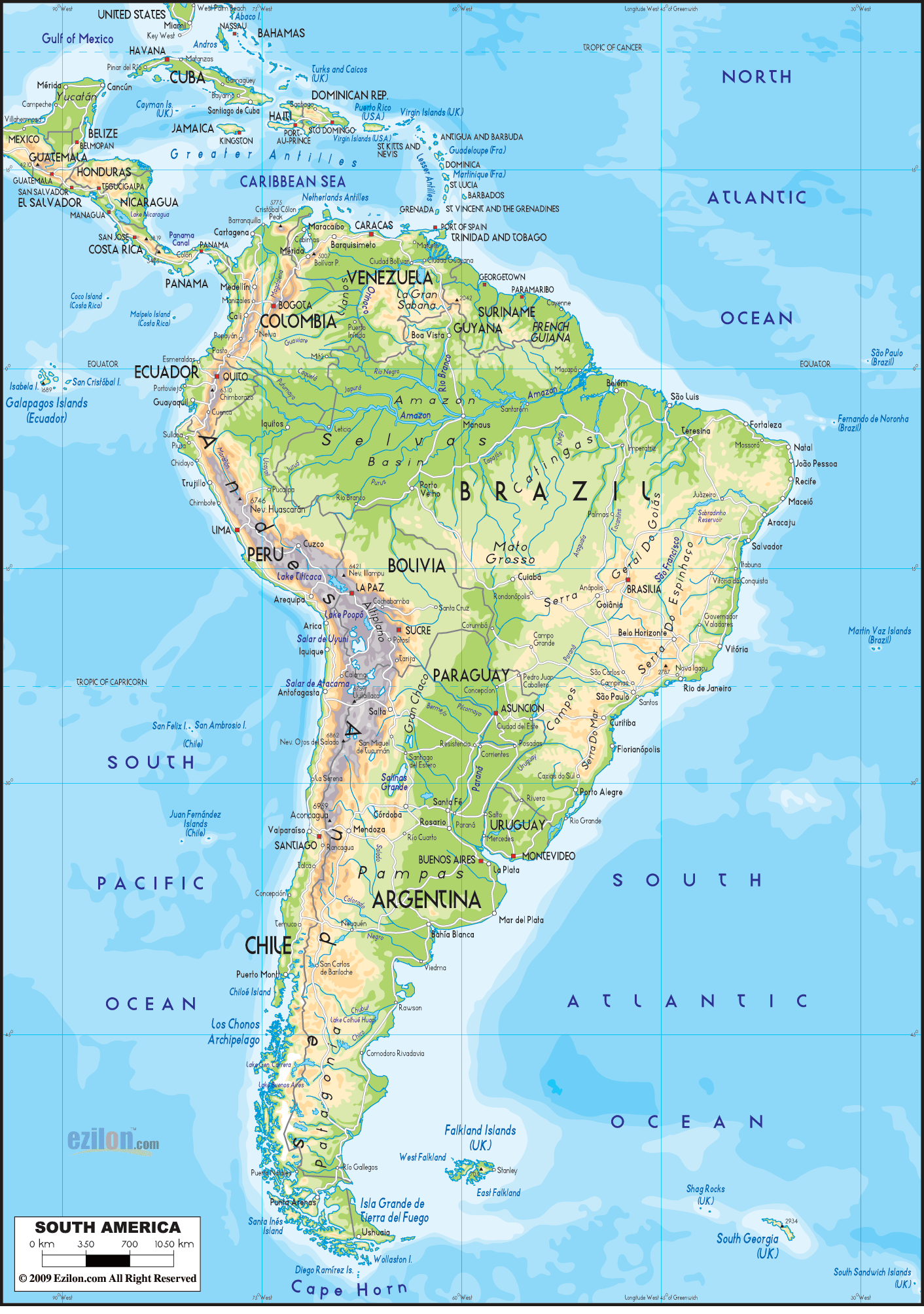

Description: The Physical Map of South America showing major geographical features like elevations, mountain ranges, deserts, seas, lakes, plateaus, peninsulas, rivers, plains, landforms and other topographic features.
The map demonstrates significant changes in the rocks and landforms of South America throughout its history. Survival necessitates the adaptation of living things to their habitats. A closer examination of its landscapes reveals a mesmerizing tapestry of tales - mountain ranges that pierce the skies, expansive rainforests teeming with life, and water bodies essential to the emergence and sustenance of ancient and modern civilizations.
The mention of South America’s elevations evokes visions of the grand Andes Mountains. This spine not only defines the continent's western edge but also serves as a testament to the raw power of plate tectonics. Extending from Venezuela in the north, through Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and finally, to Argentina in the south, the Andes is not merely a collection of peaks.
It represents varied ecosystems, from the snow-clad summits to the rich vineyards on its slopes. It encapsulates an astonishing array of life forms and human cultures that have developed symbiotic relationships with this rugged terrain over millennia.
While the towering Andes might dominate conversations, other mountainous regions of South America equally demand attention. The Venezuelan Andes, for instance, seamlessly merge with the nation's rich history, providing insights into the civilizations that once thrived in their shadow.
Further south of this physical map, the Bolivian Altiplano stands in stoic beauty. This high-altitude plateau is home to ethereal landscapes like the Uyuni Salt Flats, where horizon lines blur, making it almost indistinguishable between land and sky.
The dense, green expanse of the Amazon Rainforest stands as the Earth's verdant heart. But its significance extends beyond just its vastness. Within this lively and bustling ambiance lies many secrets and marvels awaiting exploration and revelation.
The canopies shelter numerous species, many of which remain undiscovered, while its underbelly, the forest floor, teems with life forms that display incredible adaptations to the challenging, humid environment. The harmonious cacophony of this vibrant biome narrates tales of life, evolution, and the intricate interdependence of species.
On the eastern side of this physical map, the shimmering waters of the Atlantic Ocean lap against South America's shores. It is not just an expanse of saltwater; it's a confluence of histories, ecologies, and human aspirations. Maritime routes have facilitated explorations and cultural exchanges, while its warm currents influence weather patterns and ecosystems.
To the west, the mighty Pacific Ocean presents another facet of South America’s maritime identity, where the cold Humboldt Current nourishes marine ecosystems, impacting both natural and human realms, especially the agricultural practices of nations like Peru and Chile.
Among the diverse water bodies of South America, Lake Titicaca stands out as a shimmering gem. Shared by Bolivia and Peru, it isn’t just a water reservoir; it’s a sacred space enshrined in myths and legends, where history and spirituality meld. Meanwhile, the Pantanal is a testament to nature's ability to create diverse habitats. As the world’s largest tropical wetland, it showcases nature's rhythms and cycles, supporting many species and offering unparalleled wildlife viewing opportunities.
The Brazilian Highlands break the monotony of flatlands. These aren’t just elevated terrains; they symbolize the spirit of Brazil, giving birth to several rivers, influencing climates, and underpinning unique ecosystems. Their undulating contours and valleys have witnessed the ebb and flow of civilizations and have played pivotal roles in shaping modern settlements, economies, and cultures.
The Amazon Basin paints a vast picture that captures the essence of life, water, and land in a harmonious embrace. Beyond its apparent geographical significance, it becomes a crucible for numerous ecosystems, cultures, and histories. Each tributary that snakes into the Amazon carries its own stories, echoing the rhythms of the myriad communities that call its banks home.
The rivers of South America are more than just water channels; they are the lifeblood of the continent. The Amazon River, with its unmatched expanse and volume, symbolizes the essence of South America, nurturing life and cultures along its path. Then there's the Orinoco, which weaves tales of the Venezuelan terrains, and the Paraná, a testament to the resilience and adaptability of nature and human societies in the southern regions.
The Pampas, vast stretches of fertile grasslands, tell stories of pastoral beauty and agricultural prowess. They are more than just scenic expanses; they embody the soul of Argentina and Uruguay regions central to livestock rearing, folklore, and traditional ways of life.
Amidst the blue expanse lie treasures like the Galápagos Islands. Governed by Ecuador, these volcanic outposts are not just geologically fascinating; they are evolutionary hotspots where species have forged unique paths of adaptation, providing invaluable insights into the mechanisms of natural selection. The Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) further south, apart from their biodiversity, have been at the center of geopolitical discourses, blending natural wonder with human history.
The Atacama Desert stretches across northern Chile, the stark antithesis to the Amazon's lushness. But its aridity doesn't signify lifelessness. This region, known as the driest place on Earth, is a celebration of life's tenacity, with organisms showcasing remarkable adaptations and ancient geoglyphs offering silent testimony to cultures of yore.
Amazonian Expanse: The Amazon Rainforest is the largest rainforest on Earth, covering over 5.5 million square kilometers and producing 20% of the world's oxygen.
Andean Heights: The Andes Mountains are the most extended mountain range globally, stretching over 7,000 kilometers from Venezuela to Chile.
River Giant: Regarding discharge, the Amazon River is the world's largest river, with over 1,000 tributaries.
Desert Mystery: The title for the driest desert on Earth belongs to the Atacama Desert in Chile. There have been no substantial showers in specific areas for over four centuries.
Majestic Waterfall: With no interruptions and towering at a remarkable height of 979 meters, Angel Falls in Venezuela secures its place as the world's tallest waterfall.
Grassland Expanse: The Pampas is a vast fertile lowland covering Argentina, Uruguay, and parts of Brazil, home to rich agricultural activities.
Island Wilderness: The Galápagos Islands, located off Ecuador, are renowned for their unique biodiversity, inspiring Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
Largest Wetland: The Pantanal, mainly in Brazil, is the world's largest tropical wetland and a biodiversity hotspot.
tSalted Wonder: A massive salt-covered area characterizes Salar de Uyuni's landscape in Bolivia. It holds the record for being the most extensive flat salt area globally. When it rains, it creates a beautiful, almost magical view that resembles a mirror.
Southernmost Point: Cape Horn, located on the southern tip of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, is the southernmost point of South America.
High Altitude Lake: Lake Titicaca, bordering Bolivia and Peru, is the world's highest navigable lake at 3,812 meters.
Patagonian Beauty: The Perito Moreno Glacier in Argentina's Patagonia is one of the world's few advancing glaciers, offering a dynamic and mesmerizing landscape.
Rising Flat-Topped: The tepuis, or tabletop mountains of the Guiana Highlands, are ancient geological formations, with Mount Roraima being the most famous.
Tropical Savannah: The Gran Chaco, covering parts of Argentina, Paraguay, Bolivia, and Brazil, is a hot and semi-arid lowland region.
River Phenomenon: The Meeting of Waters, where the Rio Negro and the Amazon River converge in Brazil, showcases a stark color contrast due to different sediments.
Rich Coastline: UNESCO recognizes the Valdés Peninsula in Argentina as a significant location. Its large variety of ocean dwellers, including whales, seals, and penguins, makes it immensely popular among numerous individuals.
Volcanic Activity: Ecuador's Cotopaxi is among the highest active volcanoes globally in the Andes mountain range, boasting several active volcanoes.
Fertile Wine Region: The Maipo Valley in Chile is one of South America's most prominent wine-producing regions, with a backdrop of the Andes Mountains.
Tropical Dry Forest: The Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena is a biodiversity hotspot spanning Colombia, Ecuador, and northern Peru.
Unique Current: The Humboldt Current, or Peruvian Current, is a cold, low-salinity ocean current that runs along the west coast of South America, significantly affecting the region's climate and marine life.
In all its geographical grandeur, South America emerges as a living tapestry interwoven with intricate patterns of physical terrains, water bodies, and ecological wonders. It isn't just a static piece of Earth's crust; it's a dynamic, ever-evolving entity.
Each mountain range, river, and plain holds stories of eons of geological transformations, climatic alterations, and the indomitable spirit of life in all its forms. Understanding South America's geography is akin to leafing through the pages of an epic tome that chronicles the saga of our planet, beckoning us to embrace its lessons, mysteries, and sheer beauty with reverence and awe.

Political Map of South America
Political map and map image of South America.

Road Map of South America
Road map and map image of South America.

Regional Directory of United States of America
Information and guide about United States of America and websites with American topics.

Regional Directory of Europe
Information and guide about Europe and websites with European topics.

Regional Directory of Australia
Information and guide about Australia and websites with Australian topics.